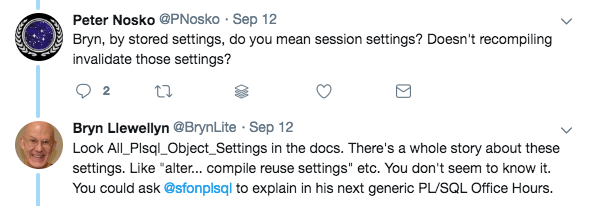
Got this plea for help via our AskTOM PL/SQL Office Hours program:
I could, at a glance, pretty well guess what the problem is.
Can you?
I am not trying to boast. I just encourage you to not read further and instead examine the code. What could be causing his problem?
Dynamic SQL can be tricky - not so much before OPEN-FOR or EXECUTE IMMEDIATE are complicated parts of the PL/SQL language. But because it's just so darned easy to mess up the SQL or PL/SQL you are constructing dynamically. You could:
This exchange then reminded me that I should write a blog post with some simple tips for making it so much easier to debug your dynamic SQL code - and ensure that it works as intended. Here goes.
In this procedure, I use a static cursor to find all matching objects, then for each object found, I execute a dynamic DDL DROP statement.
It's useful because I can drop all database objects in my schema by typing nothing more than
And it's dangerous for precisely the same reason.
Oh, but wait. Given how useful it is, maybe we should let everyone be able to use it. I know, I will run this command:
So very, very much. Let's step through my recommendations and highlight the potential problems.
1. Define your subprogram with AUTHID CURRENT_USER (invokers rights).
The procedure does not have an AUTHID clause (I bet most of your stored program units do not). This means that it defaults to "definer rights". This means that it always executes with the privileges of the definer/owner of the procedure.
Which means that if, say, HR owns drop_whatever and then SCOTT executes it (thank you, GRANT to PUBLIC!) as in:
Then SCOTT will have just dropped all of the database objects in HR's schema!
2. If you're executing dynamic DDL, make the subprogram an autonomous transaction.
The thing about DDL statements is that Oracle performs an implicit commit both before and after the DDL statement is executed. So if you have a stored procedure that executes dynamic DDL, either you have to warn everyone who might use it that any outstanding changes in their session (that's just rude) or you add this statement to your procedure:
Now, any commits (or rollbacks) executed in the procedure will affect only those changes made within the procedure.
3. Always EXECUTE IMMEDIATE or OPEN FOR a variable.
It's such a simple thing, but it could save you lots of time when trying to figure out what's wrong with your program.
Here's the thing: it's not hard to figure how to use EXECUTE IMMEDIATE. But it can be very tricky to properly construct your string at run-time. So many small mistakes can cause errors. And if you construct your string directly within the EXECUTE IMMEDIATE statement, how can you see what was executed and where you might have gone wrong?
Suppose, for example, that in the drop_whatever procedure, I constructed my DROP statement as follows:
When I try to drop my table, I see:
And what does that tell me? Not much. What option does it think I gave it that is invalid? What did I just try to do?
If, on the other hand, I assign the expression I wish to execute to a variable, and then call EXECUTE IMMEDIATE, I can trap the error, and log / display that variable (see second implementation of drop_whatever below). And then I might see something like:
Oh! I see now. I did not include a space between the object type and the object name. Silly me. So always declare a variable, assign the dynamically-constructed SQL statement to that variable, and EXECUTE IMMEDIATE it.
4. Always handle the exception that may arise from the dynamic SQL execution.
5. Log the error information plus the variable that you tried to execute.
If you don't trap the exception, you can't log or display that variable. If you don't persist that variable value, it's awfully hard to make a useful report of the problem to your support team.
You can't do much except whimper at the crappy design of your code.
6. Build a test mode into your subprogram.
I have been writing code for long and screwing up that code for so long, I have learned that it is very helpful - especially when that code makes changes to data in tables - to implement a test mode that doesn't "do" anything. Just shows me what it would have done if I'd let it.
You can see it in the code below, when I pass TRUE (the default) for the just_checking parameter.
A Much Better (?) Drop_Whatever
The "?" in that title is just to remind us that this procedure is inherently dangerous.
Here's the version of drop_whatever following my recommendations. Note that for real, production code, you should never "report" or "log" an error by calling DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE. Who's going to see that? Instead, call your standard error logging procedure and if you don't have one then get and use Logger.
As you will see in the comments, Kevan Gelling pointed out the benefit of using a template for your dynamic SQL string, with calls to REPLACE to substitute actual values for placeholders. I agree and offer yet a third implementation of drop_whatever below utilizing the approach (I won't repeat the BEGIN-END encapsulating the EXECUTE IMMEDIATE. That doesn't change.
You could also do all three of those replaces in a single assignment, but you sacrifice some readability. Thanks, Kevan, for the reminder and the code!
Let's Recap
When you write a stored program unit that contains dynamic SQL:
Dear Experts, I have below written below code:
----------------------------------------------
Declare
v_Table all_tables.TABLE_NAME%type;
v_Mnt varchar2(2):='08';
Type Cur_type is Ref Cursor;
C Cur_type;
Begin
v_Table:='ddi_ticket_10_1018';
Open C for 'SELECT * from bill.'||v_Table||v_Mnt||'Where called_nbr=123';
End;
-------------------------------------------------------------------
When executing this code, I face this Error message.
ORA-00933-SQL Command not properly ended
ORA-06512: At Line 9.
Please check the above code and modify for syntax correction
I could, at a glance, pretty well guess what the problem is.
Can you?
I am not trying to boast. I just encourage you to not read further and instead examine the code. What could be causing his problem?
Dynamic SQL can be tricky - not so much before OPEN-FOR or EXECUTE IMMEDIATE are complicated parts of the PL/SQL language. But because it's just so darned easy to mess up the SQL or PL/SQL you are constructing dynamically. You could:
- Leave out a ";" (from PL/SQL code).
- Forget to leave white space between sections of your SQL.
- Have unmatched parentheses.
- On and on and on.
In this case, I wrote back to say: "I am pretty sure you will find the problem is that you don't have a space before the "Where" keyword in:
v_Mnt||'Where called_nbr=123';This exchange then reminded me that I should write a blog post with some simple tips for making it so much easier to debug your dynamic SQL code - and ensure that it works as intended. Here goes.
- Define your subprogram with AUTHID CURRENT_USER (invokers rights).
- If you're executing dynamic DDL, make the subprogram an autonomous transaction.
- Always EXECUTE IMMEDIATE or OPEN FOR a variable.
- Always handle the exception that may arise from the dynamic SQL execution.
- Log the error information plus the variable that you tried to execute.
- Build a test mode into your subprogram.
PROCEDURE drop_whatever (nm IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT '%',
typ IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT '%')
IS
CURSOR object_cur
IS
SELECT object_name, object_type
FROM user_objects
WHERE object_name LIKE UPPER (nm)
AND object_type LIKE UPPER (typ)
AND object_name <> 'DROP_WHATEVER';
BEGIN
FOR rec IN object_cur
LOOP
EXECUTE IMMEDIATE
'DROP '
|| rec.object_type
|| ''
|| rec.object_name
|| CASE
WHEN rec.object_type IN ('TABLE', 'OBJECT')
THEN
' CASCADE CONSTRAINTS'
ELSE
NULL
END;
END LOOP;
END;
In this procedure, I use a static cursor to find all matching objects, then for each object found, I execute a dynamic DDL DROP statement.
It's useful because I can drop all database objects in my schema by typing nothing more than
EXEC drop_whatever()
And it's dangerous for precisely the same reason.
Oh, but wait. Given how useful it is, maybe we should let everyone be able to use it. I know, I will run this command:
GRANT EXECUTE ON drop_whatever TO PUBLIC
Hey what could go wrong? :-)
So very, very much. Let's step through my recommendations and highlight the potential problems.
1. Define your subprogram with AUTHID CURRENT_USER (invokers rights).
The procedure does not have an AUTHID clause (I bet most of your stored program units do not). This means that it defaults to "definer rights". This means that it always executes with the privileges of the definer/owner of the procedure.
Which means that if, say, HR owns drop_whatever and then SCOTT executes it (thank you, GRANT to PUBLIC!) as in:
EXEC HR.drop_whatever()
Then SCOTT will have just dropped all of the database objects in HR's schema!
2. If you're executing dynamic DDL, make the subprogram an autonomous transaction.
The thing about DDL statements is that Oracle performs an implicit commit both before and after the DDL statement is executed. So if you have a stored procedure that executes dynamic DDL, either you have to warn everyone who might use it that any outstanding changes in their session (that's just rude) or you add this statement to your procedure:
PRAGMA AUTONOMOUS_TRANSACTION;
Now, any commits (or rollbacks) executed in the procedure will affect only those changes made within the procedure.
3. Always EXECUTE IMMEDIATE or OPEN FOR a variable.
It's such a simple thing, but it could save you lots of time when trying to figure out what's wrong with your program.
Here's the thing: it's not hard to figure how to use EXECUTE IMMEDIATE. But it can be very tricky to properly construct your string at run-time. So many small mistakes can cause errors. And if you construct your string directly within the EXECUTE IMMEDIATE statement, how can you see what was executed and where you might have gone wrong?
Suppose, for example, that in the drop_whatever procedure, I constructed my DROP statement as follows:
EXECUTE IMMEDIATE
'DROP '
|| rec.object_type
|| rec.object_name ...When I try to drop my table, I see:
ORA-00950: invalid DROP option
And what does that tell me? Not much. What option does it think I gave it that is invalid? What did I just try to do?
If, on the other hand, I assign the expression I wish to execute to a variable, and then call EXECUTE IMMEDIATE, I can trap the error, and log / display that variable (see second implementation of drop_whatever below). And then I might see something like:
DROP SYNONYMV$SQL - FAILUREOh! I see now. I did not include a space between the object type and the object name. Silly me. So always declare a variable, assign the dynamically-constructed SQL statement to that variable, and EXECUTE IMMEDIATE it.
4. Always handle the exception that may arise from the dynamic SQL execution.
5. Log the error information plus the variable that you tried to execute.
If you don't trap the exception, you can't log or display that variable. If you don't persist that variable value, it's awfully hard to make a useful report of the problem to your support team.
You can't do much except whimper at the crappy design of your code.
6. Build a test mode into your subprogram.
I have been writing code for long and screwing up that code for so long, I have learned that it is very helpful - especially when that code makes changes to data in tables - to implement a test mode that doesn't "do" anything. Just shows me what it would have done if I'd let it.
You can see it in the code below, when I pass TRUE (the default) for the just_checking parameter.
A Much Better (?) Drop_Whatever
The "?" in that title is just to remind us that this procedure is inherently dangerous.
Here's the version of drop_whatever following my recommendations. Note that for real, production code, you should never "report" or "log" an error by calling DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE. Who's going to see that? Instead, call your standard error logging procedure and if you don't have one then get and use Logger.
PROCEDURE drop_whatever (
nm IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT '%'
, typ IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT '%'
, just_checking IN BOOLEAN DEFAULT TRUE
)
AUTHID CURRENT_USER
IS
PRAGMA AUTONOMOUS_TRANSACTION;
dropstr VARCHAR2 (32767);
CURSOR object_cur
IS
SELECT object_name, object_type
FROM user_objects
WHERE object_name LIKE UPPER (nm)
AND object_type LIKE UPPER (typ)
AND object_name <> 'DROP_WHATEVER';
BEGIN
FOR rec IN object_cur
LOOP
dropstr :=
'DROP '
|| rec.object_type
|| ''
|| rec.object_name
|| CASE
WHEN rec.object_type IN ('TABLE', 'OBJECT')
THEN ' CASCADE CONSTRAINTS'
ELSE NULL
END;
BEGIN
IF just_checking
THEN
DBMS_OUTPUT.put_line (dropstr || ' - just checking!');
ELSE
EXECUTE IMMEDIATE dropstr;
DBMS_OUTPUT.put_line (dropstr || ' - SUCCESSFUL!');
END IF;
EXCEPTION
WHEN OTHERS
THEN
DBMS_OUTPUT.put_line (dropstr || ' - FAILURE!');
DBMS_OUTPUT.put_line (DBMS_UTILITY.format_error_stack);
END;
END LOOP;
END;
As you will see in the comments, Kevan Gelling pointed out the benefit of using a template for your dynamic SQL string, with calls to REPLACE to substitute actual values for placeholders. I agree and offer yet a third implementation of drop_whatever below utilizing the approach (I won't repeat the BEGIN-END encapsulating the EXECUTE IMMEDIATE. That doesn't change.
PROCEDURE drop_whatever (
nm IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT '%'
, typ IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT '%'
, just_checking IN BOOLEAN DEFAULT TRUE
)
AUTHID CURRENT_USER
IS
PRAGMA AUTONOMOUS_TRANSACTION;
dropstr VARCHAR2 (32767) := 'DROP [object_type] [object_name] [cascade]';
CURSOR object_cur ... same as above ;
BEGIN
FOR rec IN object_cur
LOOP
dropstr := REPLACE (dropstr, '[object_type]', rec.object_type);
dropstr := REPLACE (dropstr, '[object_name]', rec.object_name);
dropstr :=
REPLACE (
dropstr,
'[cascase]',
CASE
WHEN rec.object_type IN ('TABLE', 'OBJECT')
THEN
'CASCADE CONSTRAINTS'
END);
BEGIN ... EXECUTE IMMEDIATE ... END;
END LOOP;
END;
You could also do all three of those replaces in a single assignment, but you sacrifice some readability. Thanks, Kevan, for the reminder and the code!
Let's Recap
When you write a stored program unit that contains dynamic SQL:
- Define your subprogram with AUTHID CURRENT_USER (invokers rights).
- If you're executing dynamic DDL, make the subprogram an autonomous transaction.
- Always EXECUTE IMMEDIATE or OPEN FOR a variable.
- Always handle the exception that may arise from the dynamic SQL execution.
- Log the error information plus the variable that you tried to execute.
- Build a test mode into your subprogram.